Standard Operating Procedures
Standard Operating Procedures
Configuring Work Classification
PURPOSE:
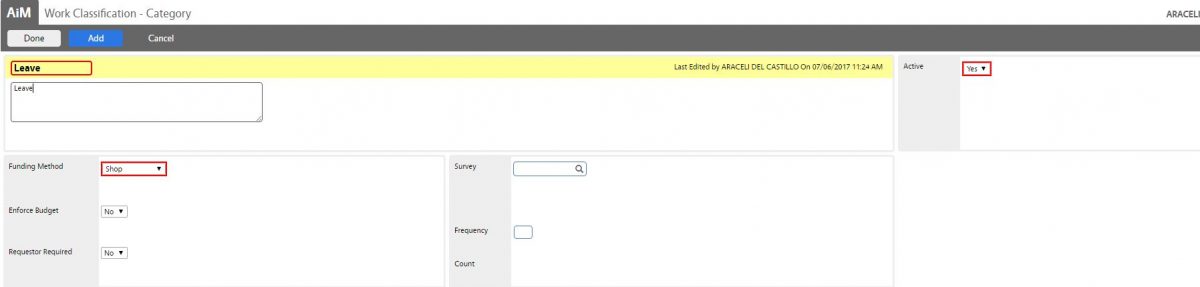
The work classification hierarchy setup determines what kind of work is to be completed. This classification is based on an organization’s business processes. Types of work (e.g., maintenance, construction, administrative, etc.) are first defined and then categories are associated to those types (e.g., within the maintenance type, categories could include preventive, deferred, service/demand, grounds, contract work, etc.). The work is defined further by associating work order statuses, phase statuses, and work codes to the categories. This classification enables the flexibility to map to any business process.
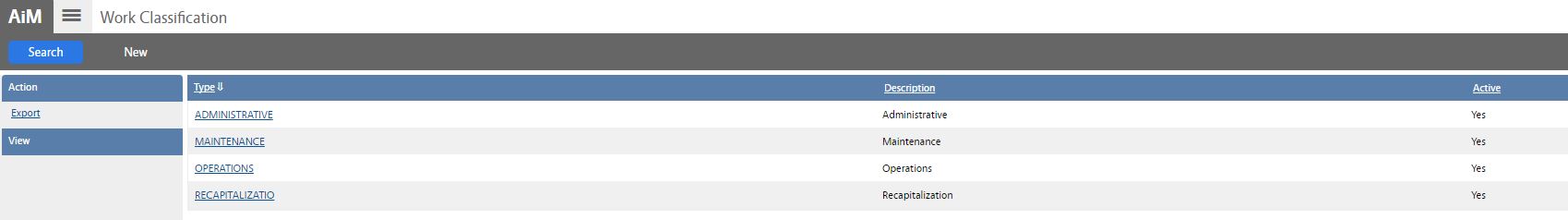
The different Work Types within AiM include the following:
| Work Types | Description |
| Maintenance | includes preventive, predictive, proactive, and corrective maintenance tasks. |
| Operations | includes access control, custodial services, event support, grounds services, moves, room setups, security, and waste management. |
| Recapitalization | includes energy conservation, estimating, fixed rate improvements, alterations, programmatic upgrades, renewal and replacement projects. |
| Administrative | includes improvement projects, leave time, shop time, and training hours for designated tasks. |
| Work Types | Category | Category Description |
| Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance (PM): | Preventive Maintenance includes planned actions undertaken to retain an item at a specified level of performance by providing repetitive scheduled tasks that prolong system operation and useful life:. This can include inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and part replacement. |
| Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance (PdM): | Predictive maintenance (PdM) is maintenance performed when empirical data that is collected and reviewed indicate that maintenance is required. Predictive Testing & Inspection (PT&I) is another term often used interchangeably to more clearly describe PdM processes. PT&I includes nondestructive and non-intrusive methods of investigation and analysis. |
| Maintenance | Proactive Maintenance (PrM): | Proactive maintenance is the sum of all maintenance work that is completed to avoid failures. |
| Maintenance | Corrective Maintenance (CM): | Maintenance activities performed because of equipment or system failure. Activities are directed toward the restoration of an item to a specified level of performance. Corrective maintenance is also referred to as demand maintenance, reactive maintenance, breakdown maintenance, etc. |
| Operations | Access | |
| Operations | Custodial SVC | |
| Operations | Event Support | |
| Operations | Grounds SVC | |
| Operations | Moves | |
| Operations | Room Setups | |
| Operations | Security | |
| Operations | Waste Mgmt | |
| Recapitalization | Capital Project Support | |
| Recapitalization | Energy Conservation | |
| Recapitalization | Fixed Rate Improvement/Alteration | |
| Recapitalization | Improvement/Alteration | |
| Recapitalization | No Charge Improvement/Alteration | |
| Recapitalization | Programmatic Upgrade | |
| Recapitalization | Renewal | |
| Recapitalization | Replacement | |
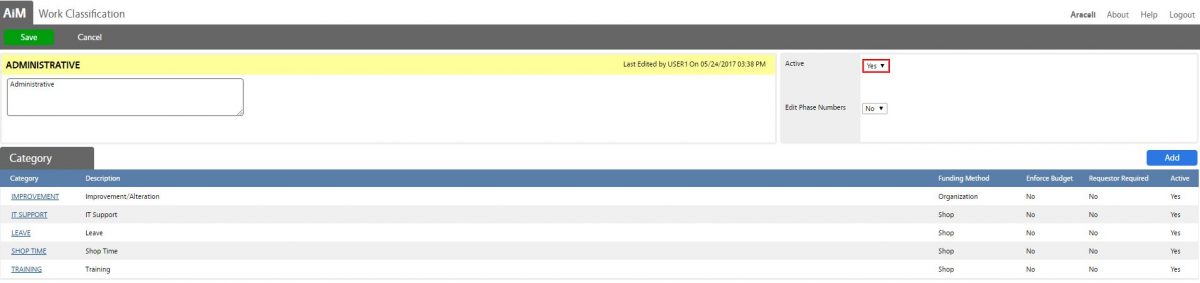
| Administrative | Improvement/Alteration | |
| Administrative | IT Support | |
| Administrative | Leave | |
| Admnistrative | Shop Time | |
| Administrative | Training |
PROCEDURE:
ROLES USED:
- System Administrator:
System Administrator is responsible for configuring and updating Work Classification (Work Types and Categories) in AiM.
Return to Work Management Module SOP